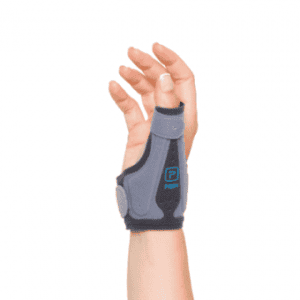
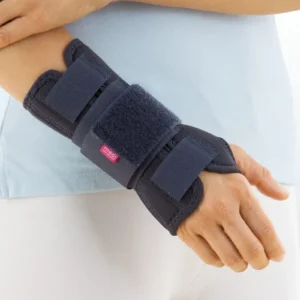
Wrist Tendonitis
Wrist Tendonitis Unlike a sprain, which is an acute ligament injury, tendonitis develops as a result of overuse or repetitive movements, resulting in inflammation of the tendons that make up the wrist joint, which causes pain and discomfort in the wrist area.
Most common pathologies
on the Hand and Wrist
Symptoms
Pain in the wrist that can extend into the forearm. Sensitivity to touch, localised swelling and difficulty moving the wrist may also occur.
Risk Factors
Activities that involve repetitive wrist movements or poor posture during them: typing on the computer for long periods of time, using hand tools that involve the use of the wrist or playing sports such as racket sports; Previous wrist injuries; Some underlying medical conditions, such as arthritis.
Protective Factors
Practising appropriate ergonomic techniques when working or carrying out activities that require wrist movements, such as: using a wrist support for either a keyboard or computer mouse; taking regular breaks for rest and stretching; and avoiding excessive repetitive movements.
Treatment
It usually involves a combination of rest, the application of local ice to reduce pain and inflammation, as well as the use of orthotics to immobilise and/or "strengthen" the wrist, which will reduce the movement of the wrist structures and allow the tendons to recover. Specific exercises to strengthen the muscles and tendons of the wrist should also be considered. In more serious or persistent cases, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Information: All the information contained here is merely a summary for a general understanding of the pathologies, highlighting their definition, symptoms, risk factors, protective measures and treatment options.
Consulting a specialised health professional is essential for an accurate diagnosis and an effective treatment plan.
Support and protection for wrist tendonitis
Discover all the orthotics for wrist tendonitis
-
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
-
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
-
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
-
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
-
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
-
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
-
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
-
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
-
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
-
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page