Collateral Ligament Rupture
Rupture of the collateral ligament, whether medial (MCL) or lateral (LCL), is an injury that affects the stability of the knee joint.
Most common knee pathologies
Symptoms
Acute pain usually occurs during the initial trauma; Oedema (swelling) may occur due to inflammation in the affected area; Sensation of lack of stability or control in the knee joint.
Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL): Isolated Rupture: Usually the result of external forces forcing the knee inwards.
Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL): Isolated Rupture: Result of external forces forcing the knee outwards.
Risk Factors
Injuries caused by side or frontal impacts. Contact sports or rapid changes of direction.
Protective Factors
Balance training and muscle strengthening contribute to stability.
Correct execution of movements and physical activities; Use of protective equipment in risk sports.
Treatment
R.I.C.E.: Rest, Ice, Compression and Elevation for initial symptom control; Specific exercises for rehabilitation and strengthening; Temporary immobilisation using splints or orthotics in severe cases; Surgical intervention may be considered in cases of more severe injuries or persistent instability.
Information: All the information contained here is merely a summary for a general understanding of the pathologies, highlighting their definition, symptoms, risk factors, protective measures and treatment options.
Consulting a specialised health professional is essential for an accurate diagnosis and an effective treatment plan.
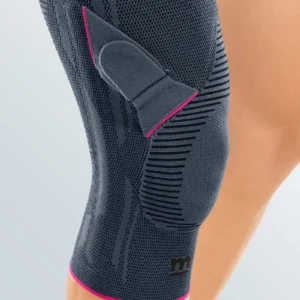
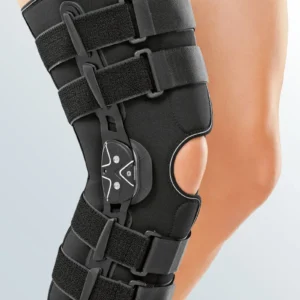
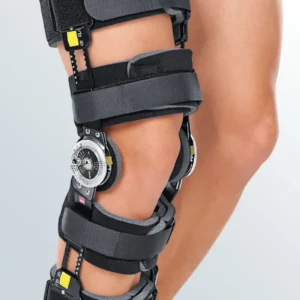
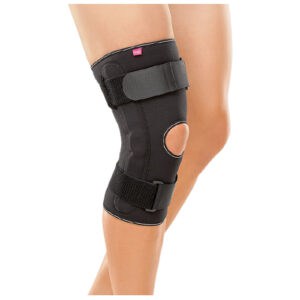
Support and protection for Collateral Ligament Rupture
Discover all the orthotics for Collateral Ligament Rupture
-
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
-
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Genumedi Simple Elastic Knee Brace for Centring the Rotula
40,70 €Avaliado 0 out of 5( 0 comentários ) -
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Genumedi PA Elasticated Knee Support for Goose Foot Tendonitis Pain Relief
61,05 €Avaliado 0 out of 5( 0 comentários ) -
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
-
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Genumedi PT Elasticated Knee Brace for Traction of the Rotator Cuff
57,00 €Avaliado 0 out of 5( 0 comentários ) -
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
-
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
-
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
-
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
-
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
-
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Protect.Co Knee Brace with Flexion and Extension Adjustment
258,00 €Avaliado 0 out of 5( 0 comentários ) -
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page