M
-
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageElasticated shin guards
23,90 € -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageProtect Abdominal Girdle
26,50 € -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageSemi-rigid Sacrolumbar Girdle
34,95 € -
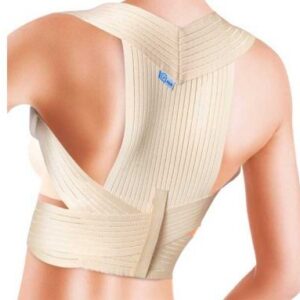 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageConfort Postural Corrector
28,90 € -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageElasticated thigh
21,90 € -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageDigital immobiliser
7,50 € -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageElasticated knee brace
25,95 € -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageMedi Posture Plus Force
162,25 € -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageMedi Posture Plus Young
103,90 € -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
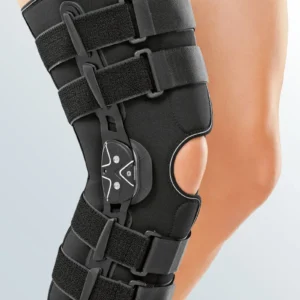 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
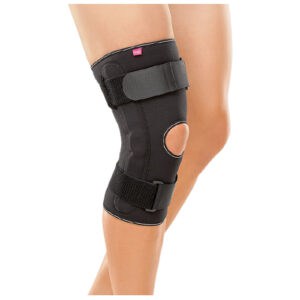 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageElasticated glove cuff
19,50 € -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pagePost-operative shoe / Barouk
19,50 € -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageShoulder action Immobiliser
105,95 € -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageSpinomed
258,85 € -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageExcellent forearm support
16,95 € -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
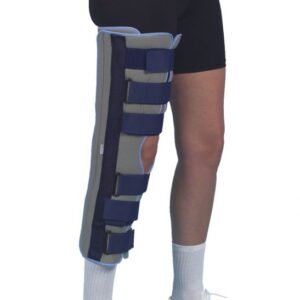 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageDepuy splint / Knee immobiliser
32,95 € -
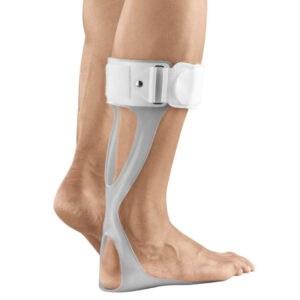 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageSpur splint with rim
22,95 € -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
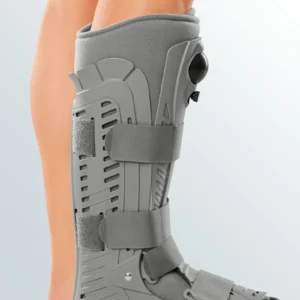
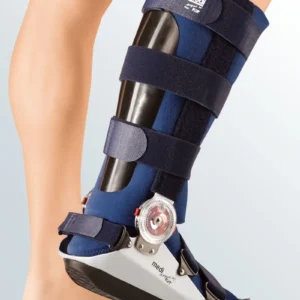
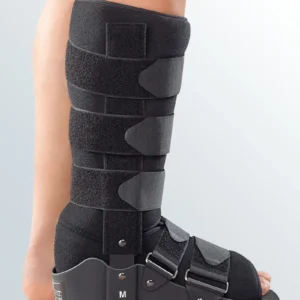 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageWalker Boot
77,36 € -
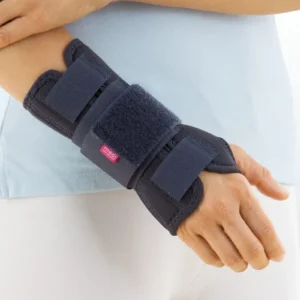 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Showing all 42 Products