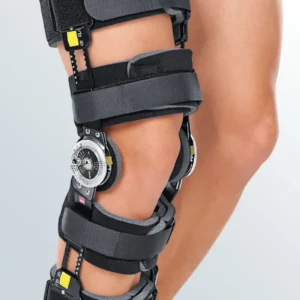
Knee arthritis
Knee arthrosis is a degenerative condition characterised by the progressive loss of cartilage in the joint, leading to symptoms such as pain and limited movement.
Most common knee pathologies
Symptoms
They develop gradually over time; Pain especially when walking, climbing stairs or performing physical activities; Stiffness in the morning or after periods of inactivity; Oedema (swelling), which can occur due to inflammation.
Risk Factors
Knee arthrosis is more common in older people; Excess weight increases the load on the knee joint; Traumas or injuries can predispose to arthrosis; Hereditary predisposition.
Protective Factors
Low-impact exercises strengthen the muscles around the knee; Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on the joint; Physiotherapy to strengthen muscles and improve range of movement.
Treatment
Specific exercises to strengthen muscles and improve joint function. Intra-articular injections with hyaluronic acid or Platelet Rich Plasma; Analgesics and anti-inflammatories to control pain and inflammation may be necessary. In advanced cases, surgery may be considered.
Information: All the information contained here is merely a summary for a general understanding of the pathologies, highlighting their definition, symptoms, risk factors, protective measures and treatment options.
Consulting a specialised health professional is essential for an accurate diagnosis and an effective treatment plan.
Support and protection for arthritic knees
Discover all the orthoses for arthrosis of the knee
-
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageGenumedi Simple Elastic Knee Brace for Centring the Rotula
40,70 €Avaliado 0 out of 5( 0 comentários ) -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageGenumedi PA Elasticated Knee Support for Goose Foot Tendonitis Pain Relief
61,05 €Avaliado 0 out of 5( 0 comentários ) -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageGenumedi PSS Elastic Knee Brace for Centralisation and Rotator Support
67,90 €Avaliado 0 out of 5( 0 comentários ) -
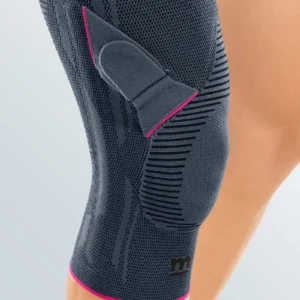 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageGenumedi PT Elasticated Knee Brace for Traction of the Rotator Cuff
57,00 €Avaliado 0 out of 5( 0 comentários ) -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
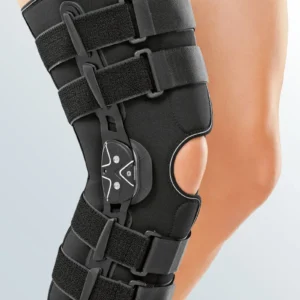 Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Seleccione Opções This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageProtect.Co Knee Brace with Flexion and Extension Adjustment
258,00 €Avaliado 0 out of 5( 0 comentários )